Bid Ask spread is one of the basic terms but people do not pay much attention to it. It’s a very important term to understand as it might affect risk reward and profitability of a trader. In this article we will understand
- Bid price meaning with examples
- Ask price meaning with examples
- What is bid ask spread
- Importance of bid ask spread
What is Bid price:
Bid Price is the price quoted by a buyer to buy a particular stock or index. So, if you want to buy a stock A at 10 Rs, then 10 Rs is your bid price or if you place a order to buy ATM call option in Bank nifty at 200 Rs then 200 Rs is your bid price.
Bid price keeps on fluctuating in the market basis demand and supply.
Example of how bid price works: Suppose stock A is in uptrend and current price is 100 Rs. Now there is a small retracement where price came down to 98 Rs. A trader has put a bid price at 95 Rs but stock started moving up after 97 Rs. Now if a trader is really interested in buying, he must move his bid price to 97 Rs otherwise he will not be able to buy.
What is Ask price:
Ask Price is the price quoted by a seller to sell a particular stock or index. So, if you want to sell a stock A at 10 Rs then 10 Rs is your ask price or if you want to sell a call option in Bank nifty at 200 Rs then 200 Rs is your ask price.
Ask price also like bid price keeps on fluctuating in the market basis demand and supply.
Example of how ask price works: Suppose stock A is in uptrend and current price is 100 Rs. As a seller, you always want to sell at higher prices so you will put ask price at 105. Now Stock A made high at 101 and then started moving down. Seller then waits for prices to come back at around 105 but when stock price is not coming up, then he can revise his ask price to exit from the stock.
Bid Ask Spread meaning:
Bid-Ask Spread in stocks or indexes is the difference between ask (Seller) price and bid (Buyer) price. We already now know that ask price is the value point at which the seller is ready to sell and bid price is the point at which a buyer is ready to buy.
When a trade takes place in marketplace: Trade happens when the two value points match in a marketplace, i.e., when a buyer and a seller agree to the prices being offered by each other then trade happens.
Example:
Suppose the price of stock A is currently at 100 Rs. Now if price moves to 102, this means there are buyers buying at 102 and there are sellers who are selling at 102. So, trade has happened at 102 because both buyer and seller have agreed a transaction at this price.
These prices are determined by demand and supply, and the gap between these two forces defines the spread between buy-sell prices. The larger the gap, the greater the spread!
So, when the market is highly liquid, spread values can be very small which means there is huge demand and huge supply, but when the market is illiquid or less liquid, spread can be large. You can compare the bid ask spread of NIFTY / BANK NIFTY as they are highly liquid and any stock which is small cap.
Why Bid Ask Spread is Important:
LIQUIDITY
When the bid and ask prices are very close, this typically means that there is ample liquidity in the security. In this scenario, the security is said to have a “narrow” bid-ask spread. This is good for traders because it makes it easier to enter or exit their positions. This becomes more important when you are trading with large positions in the market. On the other hand, securities with a “wide” bid-ask spread—that is, where the bid and ask prices are far apart.
Examples :
A less liquid stock A: Suppose current price of stock is at 10 Rs and trader want to buy at 10 Rs. If there is no seller at 10, then he will not be able to buy the stock. So now trader will see what is the ask price by seller which can be 13 Rs and this means that due to spread of 3 Rs, he must buy at higher price. This is happening because there is a gap in demand and supply
A highly liquid index (NIFTY / BANK NIFTY ) : Suppose at the money CALL price currently is 100 Rs . Now if you want to buy at 100 Rs, you will get at 100-101 because there is no problem of demand and supply. There is always a seller and buyer willing to execute the transaction.
PROFIT TARGETS AND RISK REWARD
Let us see this with example. As per below table there are 3 sellers and 2 buyers in the market at a certain price and quantity.
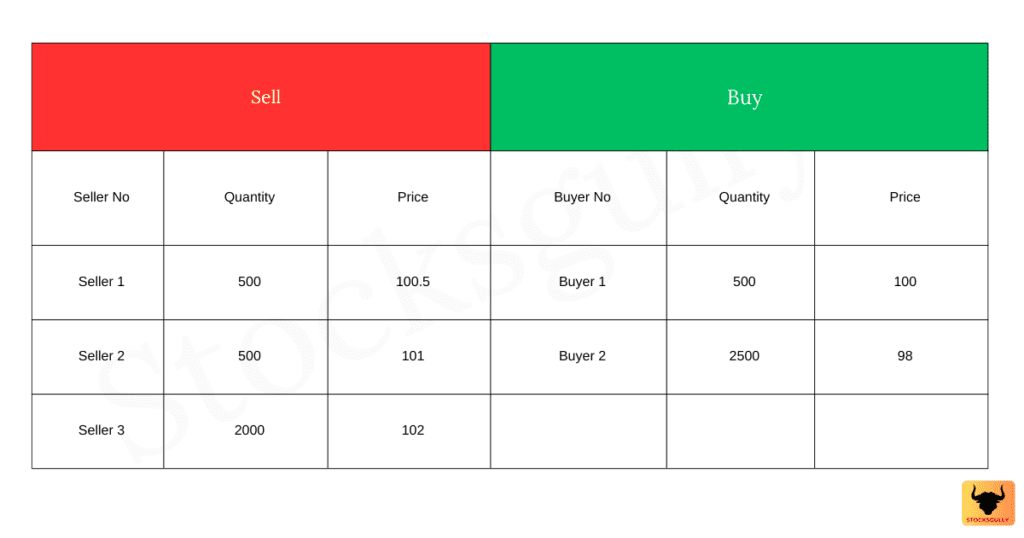
If you observe the above table, buyer bid price is lesser than the seller, ask price. Which means seller always wanted to sell at higher price and buyer always wanted to buy at lower price. Now we will see 2 scenarios:
Scenario 1: Buyer 1 wanted to buy 500 quantities. There is no seller at 100 Rs, so buyer 1 must increase the price by 0.5 Rs to buy 500 Quantities.
Scenario 2: Buyer 2 wanted to buy 2500 quantities. This will be filled at 3 different prices
- 500 quantities: 100.5 Rs ( From seller 1)
- 500 quantities: 101 Rs ( From seller 2 ) and remaining 1500 quantities at 102 Rs ( From seller 3 ) . So now it will be clear to you how bid ask spread affect in filling the orders .
Long term investors: Bid ask spread does not matter much to long term investors who are holding the stocks for many years. This is because the profit targets are high enough and bid ask spread doesn’t matter much.
Short term traders (Scalpers, Intraday and swing traders): Wide bid ask spread will affect short term traders as they enter and exit in short period of time.
This is because for their trades to become profitable, the market needs to move in their favour larger than the difference between the bid and ask prices and target price. So, suppose you want to enter the stock at 100 Rs with target of 150 Rs (You want profit of 50 Rs). Now suppose bid ask spread is 5 Rs, so target price should be 155 now to get same 100 Rs profit. The larger the bid ask spread, the larger the required price movement.
How is bid-ask spread calculated
Suppose ask price by seller is 10 Rs and bid price by buyer is 9 Rs then spread is 10-9 = 1Rs
FAQ’s
1. What is the bid-ask spread?
Bid-Ask Spread in stocks or indexes is the difference between ask (Seller) price and bid (Buyer) price.
2. Is a high bid-ask spread good?
High bid ask spread means lesser liquidity and hence lower supply and demand . If you are long term investor , then it might not matter much but for scalpers , intraday and swing traders it matters as the holding time is very less.
3. What is the bid-ask spread formula example?
Suppose ask price by seller is 10 Rs and bid price by buyer is 9 Rs then spread is 10-9 = 1Rs
4. What are the benefits of bid-ask spread?
There are 2 major benefits of narrow bid ask spread
a) Liquidity: Narrow wide spread means high liquidity and hence high demand and supply . This helps trader to get their order filling faster.
b) Risk Reward Ratio: There is more control on risk reward ratio because narrow bid ask spread will not affect the target price
5. What causes a low bid-ask spread?
A high liquidity in the market causes a low bid ask spread.
Read these article next :
- How to start trading in stock markets
- How to read candlesticks for beginners
- How to choose best time frame for trading

